ASGP (2022), vol. 92: 181–200
NODULICHNUS HUNGARICUS IGEN. ET ISP. NOV. FROM THE EARLY MIOCENE OF NORTH HUNGARY
Rozália FODOR (1*) & Árpád DÁVID (2)
1) Matra Museum of the Hungarian Natural History Museum, H-3200 Gyöngyös, Kossuth u. 40, Hungary, e-mail: neaddfellia@yahoo.com
2) University of Debrecen, Department of Mineralogy and Geology, H-4032 Debrecen, Egyetem tér 1, Hungary, e-mail: coralga@yahoo.com
*) Corresponding author
Fodor, R. & Dávid, Á., 2022. Nodulichnus hungaricus igen. et isp. nov. from the Early Miocene of North Hungary. Annales Societatis Geologorum Poloniae, 92: 181–200.
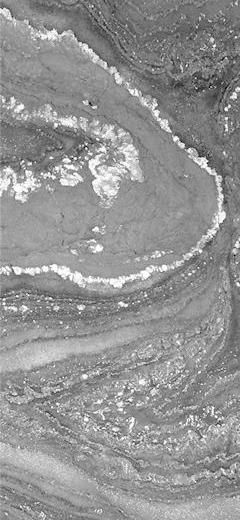
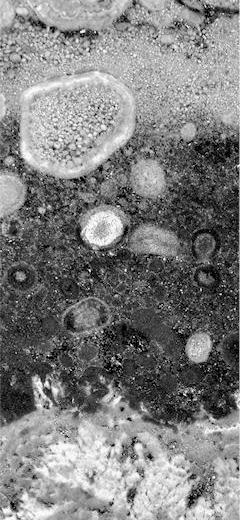
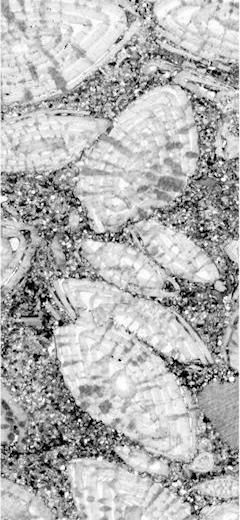
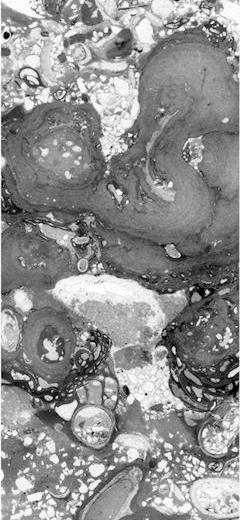
Abstract: The Early Miocene shallow-marine Salgótarján Lignite Formation of northern Hungary is host to a hitherto unknown trace fossil, here named Nodulichnus hungaricus igen. et isp. nov. This trace is a vertical, straight, or slightly winding, non-branching, tubular structure, 2–5 mm in diameter, and 50–100 mm long. It is filled with globose pellets, which are 0.5–0.6 mm in diameter. Generally, this trace fossil is isolated, but it may occur in clusters. Ethologically, it is a dwelling structure (domichnion), where the producer organism was living during high tide. Additionally, Nodulichnus hungaricus igen. et isp. nov. is accompanied by Ophiomorpha nodosa (Lundgren, 1891), Gyrolithes nodosus (Mayoral and Muñiz, 1998), Thalassinoides isp., Planolites isp. and Tomaculum problematicum (Groom, 1902), which occur sparsely at this level. The trace fossil assemblage is interpreted as being evolved in a ‘low-energy’, sandy beach setting.
Manuscript received 18 October 2021, accepted 30 March 2022