ASGP (2003), vol. 73: 183-192
GLAUCONY FROM THE CONDENSED LOWER-MIDDLE JURASSIC DEPOSITS OF THE KRIŽNA UNIT, WESTERN TATRA MOUNTAINS, POLAND
Renata JACH & Krzysztof STARZEC
Institute of Geological Sciences, Jagiellonian University, Oleandry 2a, 30-063 Kraków, Poland; R.J. e-mail: jach at ing.uj.edu.pl, K.S. e-mail: star at ing.uj.edu.pl
Jach, R. & Starzec, K., 2003. Glaucony from the condensed Lower-Middle Jurassic deposits of the Križna Unit, Western Tatra Mountains, Poland. Annales Societatis Geologorum Poloniae, 73: 183-192.
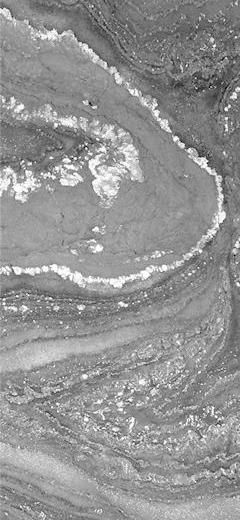
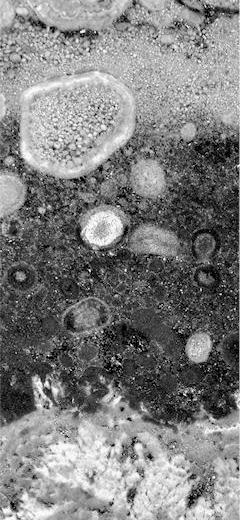
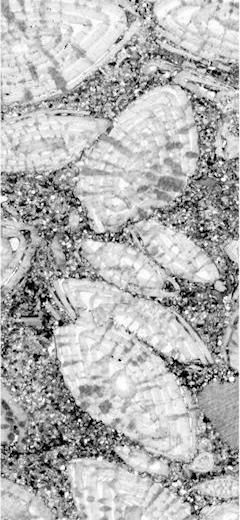
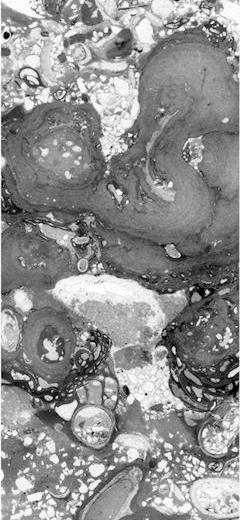
Abstract: Lower-Middle Jurassic glaucony-bearing deposits crop out in the Polish part of the Križna Unit in the Western Tatra Mts. These deposits, up to 20 cm thick, consist of glaucony-rich marls and limestones. The glaucony grains constitute up to 30% volume of the deposits. They represent an evolved stage of glauconitization since they contain more than 7% K2O. The content of Al2O3 is high (up to 19.97%, average 16.98%) while the content of Fe2O3 is low (not more than 23.48%, average 12.84%). These features are interpreted as a product of diagenetic processes. The glaucony-bearing deposits were formed at an upper bathyal depth and their rate of deposition was very low, what allowed long-lasting evolution of the glaucony grains. The K-Ar age of the glaucony grains is much younger than the biostratigraphic age of the studied section. The lowering of the K-Ar dates is interpreted as a result of loss of radiogenic Ar from the lattice of the glaucony.